Piezoelectrics are a class of functional materials that have been extensively used for application in modern electro-mechanical and mechatronics technologies. *
The sign of longitudinal piezoelectric coefficients is typically positive but recently a few ferroelectrics, such as ferroelectric polymer poly(vinylidene fluoride) and van der Waals ferroelectric CuInP2S6, were experimentally found to have negative piezoelectricity.
In the article “Tunable and parabolic piezoelectricity in hafnia under epitaxial strain” Hao Cheng, Peijie Jiao, Jian Wang, Mingkai Qing, Yu Deng, Jun-Ming Liu, Laurent Bellaiche, Di Wu and Yurong Yang, using first-principles calculation and measurements, show that the sign of the longitudinal linear piezoelectric coefficient of HfO2 can be tuned from positive to negative via epitaxial strain. *
Nonlinear and even parabolic piezoelectric behaviors are further found at tensile epitaxial strain. *
This parabolic piezoelectric behavior implies that the polarization decreases when increasing the magnitude of either compressive or tensile longitudinal strain, or, equivalently, that the strain increases when increasing the magnitude of electric field being either parallel or antiparallel to the direction of polarization. The unusual piezoelectric effects are from the chemical coordination of the active oxygen atoms. *
These striking piezoelectric features of positive and negative sign, as well as linear and parabolical behaviors, expand the current knowledge in piezoelectricity and broaden the potential of piezoelectric applications towards electro-mechanical and communications technology. *
NanoWorld Pt/Ir coated Pointprobe® EFM AFM probes were used for the sample characterization by switching spectroscopy PFM measurements.
Switching spectroscopy PFM measurements were performed on the bare HZO film surface at room temperature with Nanoworld Pointprobe® EFM in a commercially available atomic force microscope, while the LSMO electrode was grounded.
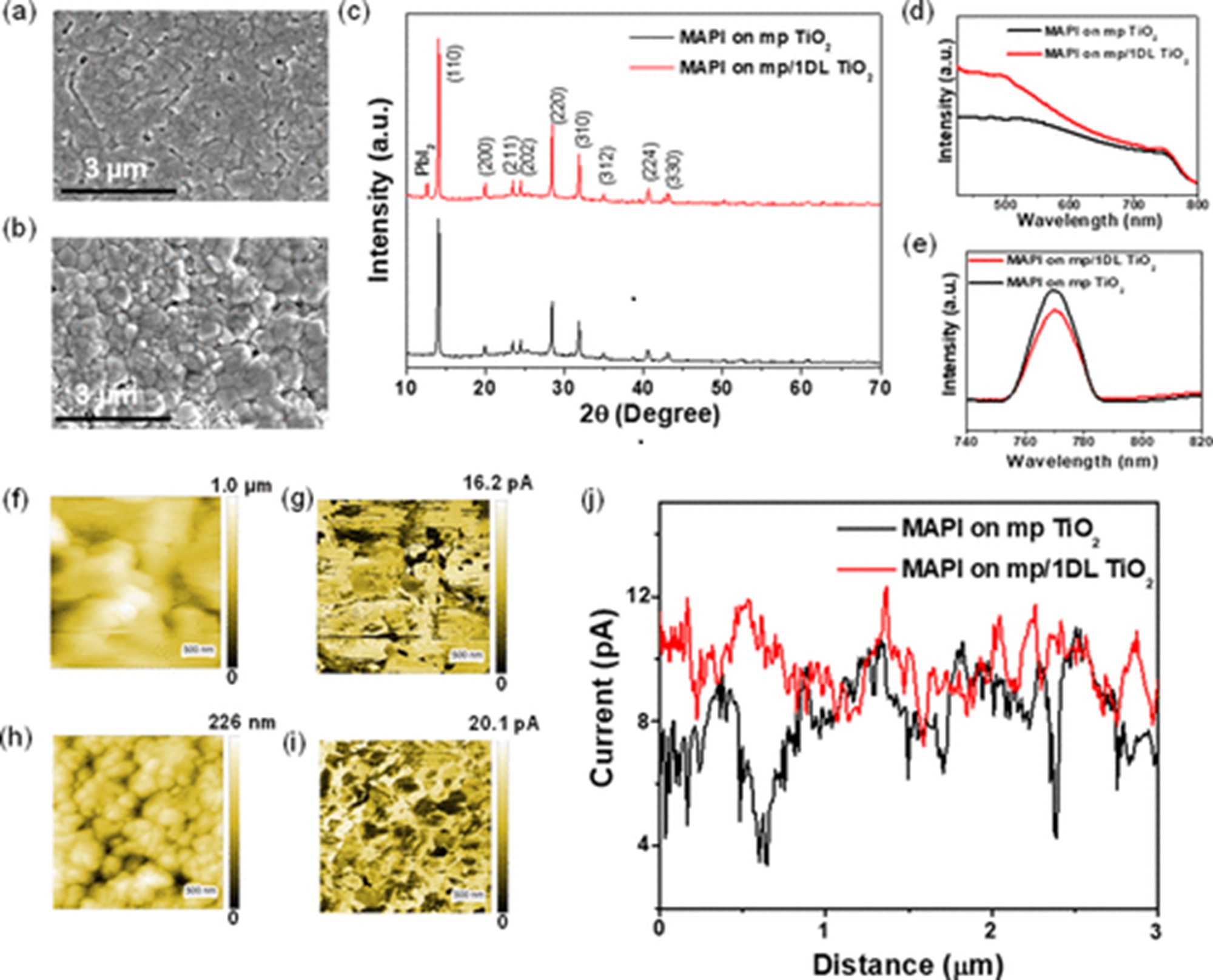
![Fig. 5 from Hao Cheng et al. (2024) “Tunable and parabolic piezoelectricity in hafnia under epitaxial strain”: [111]-oriented HZO films grown on (110) LAO substrates with different thicknesses of LSMO buffer layers.a XRD θ-2θ patterns of HZO films deposited on (110)-oriented LAO with 20-, 33-, 66-nm-thick LSMO buffer layers. b PFM phase loops of the HZO films deposited on 20-, 33- and 66-nm-thick LSMO buffered LAO substrates. c–e Reciprocal space mappings around the (310) spot of HZO/LSMO/LAO with c 20-, d 33-, and e 66-nm-thick LSMO buffer layers. NanoWorld Pt/Ir coated Pointprobe® EFM AFM probes the sample characterization by switching spectroscopy PFM measurements.](https://www.nanoworld.com/blog/wp-content/uploads/2025/05/Fig-5-from-Hao-Cheng-et-al-2024-Tunable-and-parabolic-piezoelectricity-in-hafnia-under-epitaxial-strain-NanoWorld-EFM-AFM-probe-blog.jpg)
Fig. 5 from Hao Cheng et al. (2024) “Tunable and parabolic piezoelectricity in hafnia under epitaxial strain”: [111]-oriented HZO films grown on (110) LAO substrates with different thicknesses of LSMO buffer layers.
a XRD θ-2θ patterns of HZO films deposited on (110)-oriented LAO with 20-, 33-, 66-nm-thick LSMO buffer layers. b PFM phase loops of the HZO films deposited on 20-, 33- and 66-nm-thick LSMO buffered LAO substrates. c–e Reciprocal space mappings around the (310) spot of HZO/LSMO/LAO with c 20-, d 33-, and e 66-nm-thick LSMO buffer layers.
Tunable and parabolic piezoelectricity in hafnia under epitaxial strain
Nature Communications volume 15, Article number: 394 (2024)
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-023-44207-w
Open Access The article “ Tunable and parabolic piezoelectricity in hafnia under epitaxial strain ” by Hao Cheng, Peijie Jiao, Jian Wang, Mingkai Qing, Yu Deng, Jun-Ming Liu, Laurent Bellaiche, Di Wu and Yurong Yang is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons license, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons license and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this license, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.