Type: CONTSC
Contact Mode – Short AFM Cantilever

| Cantilever Data | Value | Range* |
|---|---|---|
| Resonance Frequency | 25 kHz | 10 - 39 kHz |
| Force Constant | 0.2 N/m | 0.02 - 0.7 N/m |
| Length | 225 µm | 220 - 230 µm |
| Mean Width | 48 µm | 42.5 - 52.5 µm |
| Thickness | 1 µm | 0.5 - 1.5 µm |
*Typical values
This AFM probe has alignment grooves on the back side of the support chip.
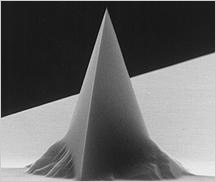
Pointprobe® AFM tip
NanoWorld® Pointprobe® CONTSC AFM probe is an alternative AFM cantilever type for contact mode applications. The length of AFM cantilever is reduced with respect to the preferred contact mode type enabling easier exchange with non-contact mode probes for some AFM instruments. Additionally, this AFM probe type allows the application for lateral or friction force mode.
All SPM and AFM probes of the Pointprobe® series are made from monolithic silicon which is highly doped to dissipate static charge. They are chemically inert and offer a high mechanical Q-factor for high sensitivity. The AFM tip is shaped like a polygon based pyramid with a typical height of 10 - 15 µm.
Additionally, this AFM probes offers typical AFM tip radius of curvature of less than 8 nm.
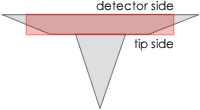 A trapezoidal cross section of the AFM cantilever and therefore 30% wider (e.g. NCH) AFM cantilever detector side result in easier and faster laser adjustment. Additionally, because there is simply more space to place and reflect the laser beam, a higher SUM signal is reached.
A trapezoidal cross section of the AFM cantilever and therefore 30% wider (e.g. NCH) AFM cantilever detector side result in easier and faster laser adjustment. Additionally, because there is simply more space to place and reflect the laser beam, a higher SUM signal is reached.
Tip shape: Standard
Coating: none
| Order Code | Quantity | Data Sheet |
|---|---|---|
| CONTSC-10 | 10 | yes |
| CONTSC-20 | 20 | yes |
| CONTSC-50 | 50 | no |
| CONTSC-W | 380 | yes |
NanoWorld® Pointprobe® Silicon AFM Probes Screencast (Standard AFM Tip)
Subscribe to NanoWorld® Youtube Channel
For more information contact: info@nanoworld.com
Pointprobe® is a registered trademark of NanoWorld AG
All data are subject to change without notice.
NanoWorld AG
Rue des Saars 10
CH-2000 Neuchâtel,
Switzerland
www.nanoworld.com
For detailed information about our AFM probe product series please see below:








 POINTPROBE®
POINTPROBE®
 ARROW™
ARROW™
 ULTRA-SHORT CANTILEVERS
ULTRA-SHORT CANTILEVERS
 PYREX-NITRIDE
PYREX-NITRIDE
 COATINGS
COATINGS
